Retina
What is the Retina?
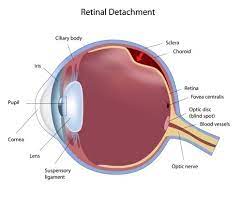
The retina is located in the inner-most part of the eye. It contains the light sensitive part of your eyes, and the nerve tissue and cellular networks needed for vision. The retina contains two types of cells that absorb the light needed for vision: Rods and Cones. The rods enable us to see in dim light and allow for black and white vision. The cones enable us to see in well-lit areas and are responsible not only for color vision, but for high-definition vision as when reading small print or working on a computer.
The retina also contains ganglion cells, that among other things, contribute to the circadian rhythms (or sleep/wake cycle) of your body.
When light enters the eye and then gets absorbed by the retina, it is converted into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then transmitted to your brain through the optic nerve. The optic nerve takes these electrical signals to the visual cortex (located at the back of our brains). It is in the visual cortex that those electrical signals are converted into and interpreted as sight.
The human retina is extremely complex. It’s made of 10 different layers, and each layer is either directly or indirectly responsible for vision. The retina also houses a number of blood vessels, as all the nerves need a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients found in blood. If there is a problem with the flow of blood to the retina, it can mean major problems for your vision. These vision problems can range from blurry vision to complete blindness. Common conditions that affect blood flow to your eyes are High Blood Pressure, Diabetes, and High Cholesterol (Atherosclerosis), among others.
Retinal Conditions
The blood supply is just one part of the retina that can cause major problems with vision. A list of common problems that ophthalmologists and retina specialists treat would contain the following:
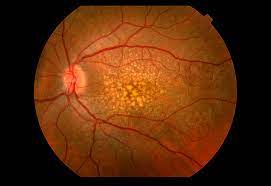
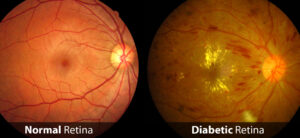
Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic Retinopathy is a condition that is a complication of diabetes that can damage the retina. The patient may not notice any symptoms in the beginning, but symptoms can appear later. Diabetes can cause bleeding, swelling and/or scarring in the retina. This condition can lead to blindness if left untreated. It can cause many symptoms, but the most common are blurry vision, reddening of vision, vision loss, eye pain, etc.
Flashes and Floaters: Flashes and floaters can be a sign of a retinal tear or retinal detachment. If you are experiencing these symptoms, one should see an eye care specialist urgently.
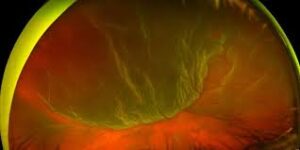
Retinal Tear/Retinal Detachment: Retinal tears or retinal detachments can happen when the retina is torn or separated from the underlying support tissue. These are serious conditions that can threaten your vision, and one should see an eye care specialist urgently.
Macular Degeneration: Macular Degeneration results from deterioration of the light receptors (rods and cones) in the innermost layer of the retina. Symptoms can include blurred or distorted vision, and central vision loss. Macular Degeneration has a genetic component and can run in families. If left untreated, this condition can cause blindness.
In addition to this list, there are many conditions related to the Retina that cause patients to see a Retina specialist. Some of these conditions can threaten your vision and require immediate attention.